
What is Bronchiectasis?
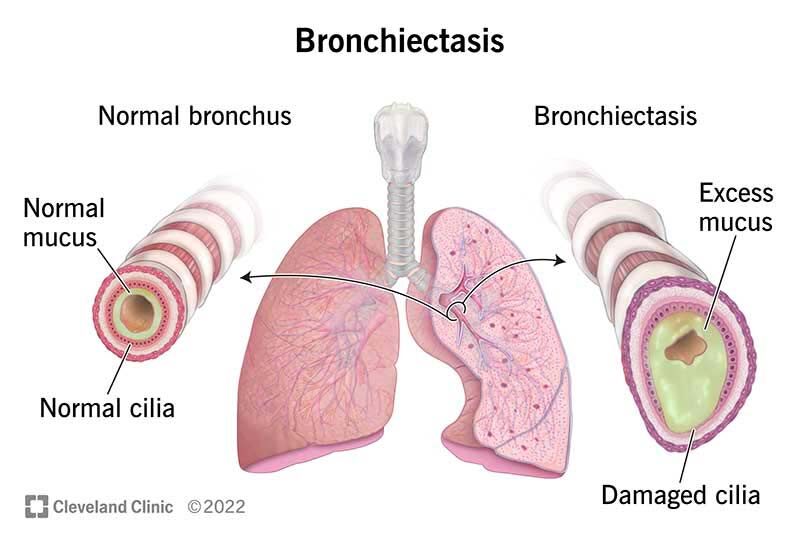
Bronchiectasis is a condition that involves damage and scarring of the lungs, specifically the airways known as bronchi. This condition can arise due to various factors, but it’s commonly associated with previous lung infections or illnesses. Imagine the bronchi as the passageways that carry air to and from your lungs. When these airways become damaged or scarred, they can widen and lose their natural elasticity, leading to bronchiectasis.
Causes and Development
One common cause of bronchiectasis is post-infective lung damage. For instance, if a person has experienced recurrent lung infections or pneumonia, even after recovery, there might be lingering scarring left behind. This scarring can contribute to the development of bronchiectasis over time.
After an infection subsides, the scarring may persist, affecting the structure of the bronchi. Consequently, the damaged bronchi might become wider and less efficient in clearing mucus and debris from the lungs. This combination of scarring and enlarged airways characterizes bronchiectasis.
Another scenario where bronchiectasis can occur is in individuals who have previously had tuberculosis (TB). Although they might recover from the active phase of TB, the residual scarring can linger and lead to the development of bronchiectasis.
Impact on Lung Function
In bronchiectasis, the scarring and dilation of the airways can hinder the normal clearance of mucus and particles from the lungs. This impairment can result in persistent symptoms such as coughing, production of excessive mucus, and even difficulty breathing.
The link between scarring, dilation, and bronchiectasis underscores the importance of understanding the condition’s origins. Recognizing the role of prior infections and lung damage is crucial for both medical professionals and individuals seeking to manage and prevent bronchiectasis.
As we explore deeper into the symptoms, causes, treatments, and prevention strategies associated with bronchiectasis, we gain valuable insights into how to address and manage this condition effectively. By understanding bronchiectasis, we empower ourselves to take proactive steps in maintaining our lung health.
Bronchiectasis vs. Bronchitis: What Is The Difference?
Bronchiectasis and bronchitis may share similarities in their names, but they are distinct respiratory conditions. Let’s delve into what sets them apart:
Bronchiectasis: Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung condition where the airways become permanently widened and scarred. This can lead to a buildup of mucus, making it difficult to clear the airways. Symptoms often include a persistent cough with thick, copious mucus, recurrent lung infections, and shortness of breath. Bronchiectasis is usually a result of underlying issues like infections, immune deficiencies, or genetic factors. Diagnosis involves imaging tests and lung function assessments, while treatment focuses on managing symptoms, preventing infections, and promoting lung health through medications, physiotherapy, and vaccination.
Bronchitis: Bronchitis, on the other hand, is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes – the air passages that carry air to the lungs. It can be acute or chronic. Acute bronchitis is often caused by viral infections and leads to a temporary cough with clear or discolored mucus, chest discomfort, and sometimes low-grade fever. Chronic bronchitis is a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and is primarily caused by smoking. It involves persistent cough with mucus production for at least three months a year, two years in a row. Diagnosis includes physical examination, medical history, and sometimes imaging. Treatment involves managing symptoms, quitting smoking, and lifestyle adjustments.
In essence, while both conditions affect the respiratory system and may involve coughing and mucus, bronchiectasis is characterized by permanent airway damage and scarring, whereas bronchitis primarily involves inflammation of the air passages. If you experience respiratory symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Symptoms of Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis, characterized by lung scarring and damage to the airways, presents a range of distinctive symptoms that can significantly impact an individual’s daily life. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management.
Persistent Chesty Cough
One of the classic symptoms of bronchiectasis is a persistent, chesty cough. Individuals with this condition often find themselves coughing frequently throughout the day. In some cases, this cough can occur up to 10 or 20 times a day. The cough is typically characterized by the production of mucus, contributing to the term “chesty” cough. This excessive mucus production is a result of the damaged airways struggling to effectively clear mucus from the lungs.
Changes in Phlegm
The nature of the cough in bronchiectasis patients often leads to the production of significant amounts of mucus. This mucus is usually white in color. However, when secondary infections occur—bacterial or viral—the phlegm may change in color. It can become yellowish or greenish, indicating the presence of infection. Monitoring the color and consistency of phlegm can provide valuable insights into the state of the condition.
Chest Discomfort and Pain
The act of prolonged and forceful coughing in bronchiectasis patients can exert pressure on the muscles of the chest wall. Over time, this persistent pressure can lead to discomfort and pain in the chest area. The muscles, strained from continuous coughing, can become fatigued, resulting in aching sensations. This discomfort adds an extra layer of challenge to the daily lives of individuals living with bronchiectasis.
Understanding the Interconnection of Symptoms
These symptoms interconnect, forming a complex web that characterizes bronchiectasis. The persistent cough, excessive mucus, and chest discomfort can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. It’s important for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek medical attention for proper evaluation and management.
As we delve further into the causes, risk factors, treatments, and preventive measures associated with bronchiectasis, we equip ourselves with the knowledge to navigate this condition effectively. Recognizing the symptoms is a vital step toward proactive lung health management.
Who Is At Risk To Get Bronchiectasis And Why?
Bronchiectasis isn’t a condition that discriminates—it can affect anyone. However, certain risk factors make individuals more susceptible to its development. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for identifying potential vulnerabilities and taking proactive steps toward prevention and management.
Post-Infective State: A Common Trigger
History of respiratory infections, such as pneumonia, tuberculosis (TB), or even a previous bout of COVID-19, can increase the risk of developing bronchiectasis. When the lungs endure an infection, scarring can occur as part of the healing process. This scarring can damage the airways, setting the stage for bronchiectasis.
Weakened Immune Systems: An Added Vulnerability
Individuals with weakened immune systems are at a heightened risk of bronchiectasis. This includes individuals with conditions like cancer, diabetes, or HIV. A genetically inherited low immune system, often termed immune deficiency disorder, can also play a role. When the body’s defenses against infections are compromised, recurrent infections can occur more easily. This repetitive assault on the lungs can lead to the development of scarring and bronchiectasis.
The Domino Effect of Low Immunity
Low immunity doesn’t just make infections more likely—it also makes their impact more severe. When infections occur, the immune response may not be robust enough to completely eliminate the invading pathogens. This incomplete resolution can lead to lingering inflammation and damage to lung tissues, eventually resulting in bronchiectasis.
Post-Viral Infections: A Lesser-Known Culprit
While we often associate bronchiectasis with bacterial infections, certain viral infections can also contribute. Following illnesses like measles, mumps, or rubella, the body’s immune response can inadvertently damage lung tissues during the fight against the virus. This damage can set the stage for bronchiectasis, even after the viral infection has been overcome.
The Path Forward: Awareness and Vigilance
Awareness of these risk factors empowers individuals to take proactive steps in safeguarding their lung health. For those with a history of infections or compromised immunity, regular medical check-ups and timely interventions can make a substantial difference. By staying vigilant and informed, we can mitigate the risk of bronchiectasis and its potential impact on our respiratory well-being.
Diagnosing Bronchiectasis
Diagnosing bronchiectasis begins with a careful examination of the patient’s history and physical signs. Detecting the condition early is key to effective management and preserving lung health. Here’s how doctors unravel the clues to diagnose bronchiectasis:
1. History: Piecing Together the Puzzle
When a patient presents with a prolonged cough or recurrent lung infections, it raises a suspicion of bronchiectasis. The history of such symptoms serves as a crucial starting point for diagnosis. Additionally, a history of previous respiratory infections, pneumonia, or chronic conditions like tuberculosis can provide valuable insights.
2. Physical Examination: Listening for Telltale Sounds
During a physical examination, healthcare professionals listen closely to the sounds of the lungs. The distinctive “krckrckrc” crackling sounds heard through a stethoscope can be indicative of bronchiectasis. These sounds result from the air passing through the dilated and scarred airways of the lungs.
3. Chest X-ray: Capturing Visual Clues
A chest X-ray is a valuable diagnostic tool in bronchiectasis. It may reveal dilated bronchial tubes and patterns resembling tram lines, which are characteristic features of the condition. These tram line patterns are visible due to the airway dilation and scarring that are hallmarks of bronchiectasis.
4. CT Scan: A Deeper Dive
For a more detailed assessment, doctors often recommend a computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest. This imaging technique provides a clearer view of the lung structures. In bronchiectasis cases, a CT scan may reveal dilated bronchioles and bronchi, often referred to as the “signet ring sign.” This specific feature further confirms the presence of bronchiectasis.
5. Pulmonary Function Tests: Assessing Lung Capacity
Pulmonary function tests may also be conducted to gauge lung function. While these tests don’t directly diagnose bronchiectasis, they help assess the extent of lung impairment caused by the condition. Reduced lung capacity and impaired airflow can be indicative of bronchiectasis.
Discovering the Bigger Picture
Diagnosing bronchiectasis involves carefully piecing together information from history, physical examination, imaging, and sometimes lung function tests. The combination of these approaches allows healthcare professionals to uncover the presence of bronchiectasis, enabling timely interventions and the initiation of appropriate treatment strategies. Early diagnosis contributes to better outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals living with this lung condition.
How Is Bronchiectasis Treated & Managed?
Effective management of bronchiectasis involves a personalized approach based on the patient’s symptoms and specific needs. Here’s a closer look at the strategies employed to treat bronchiectasis:
1. Antibiotics for Infections
Patients experiencing recurrent bacterial infections are often prescribed antibiotics. These medications help combat bacterial growth and prevent further lung infections. Administering antibiotics can alleviate symptoms and reduce the frequency of infections, contributing to improved lung health.
2. Mucolytics and Medications for Phlegm
For patients with excessive phlegm production but no signs of infection, mucolytics may be recommended. Mucolytics are medications designed to thin and loosen mucus, making it easier to clear from the airways. Additionally, medications like Bromhexine can help manage phlegm by promoting its clearance or drying it out.
3. Managing Blood in Phlegm
If a patient presents with blood-stained phlegm or coughing up blood, specific measures are taken to address this concern. Medications such as tranexamic acid may be prescribed to help control and minimize bleeding from the bronchiectasis. This approach aims to improve patient comfort and prevent excessive blood loss.
4. Addressing Severe Bleeding and Blood Clots
In cases where patients experience severe bleeding with blood clots during coughing, hospitalization is necessary. This critical situation requires prompt intervention. A procedure called bronchial artery embolization is employed to halt bleeding. This procedure involves inserting medication into the bronchial arteries to stop blood flow and control bleeding. This intricate procedure is carried out by interventional radiologists, specialized medical professionals skilled in such techniques.
Personalized Care for Enhanced Well-being
The treatment of bronchiectasis is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Healthcare professionals tailor interventions to address each patient’s unique symptoms and needs. By addressing infections, managing excessive phlegm, and tackling complications like bleeding, healthcare providers aim to enhance lung health, improve quality of life, and minimize the impact of bronchiectasis on daily activities. Collaboration between patients and their medical team plays a pivotal role in achieving optimal outcomes and maintaining respiratory well-being.
Complications of Untreated Bronchiectasis: Managing Hemoptysis
Bronchiectasis, if left unmanaged, can lead to various complications, and one of the most critical ones is massive hemoptysis. Hemoptysis refers to coughing up blood from the respiratory tract, and when it becomes significant, it can have serious implications for the patient’s health. Here’s an overview of the potential complications associated with massive hemoptysis and the urgency of seeking medical care:
1. Hypotensive Shock and Respiratory Distress
In cases of massive hemoptysis, where a substantial amount of blood is coughed up during episodes of coughing, the loss of blood can lead to a significant drop in blood pressure. This condition, known as hypotensive shock, can result in a medical emergency. As blood pressure decreases, the heart may beat faster to compensate for the lowered pressure. Respiratory distress can also occur due to the presence of blood in the airways, hindering normal breathing patterns.
2. Immediate Intervention: Intubation and Mechanical Ventilation
When a bronchiectasis patient experiences massive hemoptysis accompanied by hypotensive shock and respiratory distress, immediate medical intervention is essential. The patient may need to be intubated, which involves inserting a tube into the airway to assist with breathing. Mechanical ventilation, through a ventilator, ensures that oxygen reaches the lungs and facilitates proper breathing. Intubation and mechanical ventilation aim to stabilize the patient’s condition and prevent further complications.
3. Life-Threatening Risks
If massive hemoptysis is not promptly managed, it can lead to a cascade of life-threatening events. Severe bleeding, lowered blood pressure, and compromised respiratory function can result in a cardiorespiratory arrest—a situation where the heart and breathing stop. In such cases, without immediate medical intervention, the outcome can be fatal.
4. Urgent Hospitalization and Treatment
Given the severity of complications associated with massive hemoptysis in bronchiectasis patients, it is imperative to seek urgent medical attention. Immediate hospitalization is necessary for proper evaluation, intervention, and treatment. Healthcare professionals will work to control the bleeding, stabilize blood pressure, and address any other concurrent health issues.
Prioritizing Respiratory Health
Bronchiectasis patients, particularly those who experience significant hemoptysis, need to be vigilant about any changes in symptoms, especially coughing up blood. Recognizing the signs of massive hemoptysis and seeking immediate medical care can be life-saving. Effective communication with healthcare providers and timely interventions play a crucial role in managing complications and ensuring optimal respiratory health for individuals with bronchiectasis.
Patient Story #1: Managing Hemoptysis in Bronchiectasis
A recent case sheds light on the critical nature of managing complications related to bronchiectasis. In this scenario, a patient’s underlying bronchiectasis, coupled with her medical history, led to a life-threatening situation. Here’s a closer look at the case and the steps taken to ensure her recovery:
Patient Profile and History
The patient, a woman in her 50s, had a history of breast cancer. Having recently completed chemotherapy and undergoing radiotherapy, her health journey was already complex. Over the past 10 years, she had experienced occasional bouts of mild coughing. Despite these challenges, her overall health was manageable.
Emergence of Alarming Symptoms
However, things took a dramatic turn when the patient started coughing up fresh blood in her phlegm. This sudden and profuse bleeding raised concerns. Despite attempting to manage the bleeding with tablet medication, her condition worsened. Coughing up significant amounts of blood—about five cups—prompted the need for immediate medical attention.
Intervention and Treatment
The patient’s condition necessitated swift and comprehensive intervention. To safeguard her airway and prevent aspiration of blood clots, a tube was inserted, securing her breathing. Mechanical ventilation was initiated to support her respiratory function. This two-day intubation period allowed the medical team to stabilize her condition and plan further steps.
Targeted Diagnosis and Treatment
A critical step in the patient’s recovery journey involved a detailed CT scan. This scan aided in identifying the precise location of the bleeding vessels. Collaborating with interventional radiologists, a procedure known as Bronchial Artery Embolization (BAE) was performed. Through this technique, specialized medication was administered directly to the bleeding area, effectively halting the bleeding and stabilizing her condition.
Recovery and Discharge
Thanks to the rapid response, focused diagnosis, and targeted treatment, the patient gradually recovered. The bleeding was successfully stopped, and her respiratory health was restored. After a period of observation and care, she was deemed well enough to be discharged and continue her recovery at home.
Importance Of Early Treatment
This real-life case underscores the importance of early intervention and specialized care for bronchiectasis patients, especially when confronting complications like massive hemoptysis. The collaboration between medical experts, the use of advanced techniques, and the patient’s resilience collectively contributed to a successful recovery. It’s a reminder that swift action and effective treatment can make all the difference in managing complex respiratory conditions.
Patient Story #2: Navigating Bronchiectasis After TB
The healthcare landscape is replete with unique patient stories that underscore the intricacies of medical conditions. Here’s an insightful look into the journey of a resilient 60-plus-year-old woman who faced both tuberculosis (TB) and subsequent bronchiectasis, emerging on the path to recovery:
Initial Encounter: A Prolonged Cough
The patient’s journey began with a persistent and nagging cough that had persisted for several months. Concerned about her health, she sought medical attention. A comprehensive evaluation, including a CT scan and bronchoscopy, revealed the presence of tuberculosis. This discovery marked the first step in addressing her health challenges.
TB Treatment and Recovery
Following the diagnosis, the patient embarked on a dedicated journey of TB treatment. She completed her treatment regimen successfully and was eventually discharged, with her health showing promising signs of improvement. The tenacity to overcome TB was a testament to her determination and the effectiveness of the medical intervention.
Unexpected Turn: Coughing Blood Clots
However, the story didn’t end there. Several months after her recovery from TB, the patient faced a new challenge: she began coughing up blood clots. This alarming symptom prompted another round of medical investigation. A CT scan provided crucial insights, revealing anomalies in her lung blood vessels that required prompt intervention.
Intervention and Collaborative Care
In response to the identified abnormalities, a collaboration with interventional radiologists was initiated. The procedure known as Bronchial Artery Embolization (BAE) was employed to address the issue. This targeted approach involved precise administration of medication to the affected area, ultimately rectifying the abnormality and averting potential complications.
The Journey to Recovery
Guided by meticulous medical care, antibiotic treatment, and therapeutic interventions, the patient’s health took a positive turn. The prescribed blood clot medication, tranexamic acid, played a crucial role in facilitating her recovery. With each step of the journey marked by resilience and dedicated medical expertise, the patient’s condition improved.
A Remarkable Triumph
The patient’s story encapsulates the intricate interplay of medical challenges and triumphs. From confronting tuberculosis to navigating bronchiectasis, her journey underscores the significance of early detection, timely intervention, and holistic care. It serves as a reminder that healthcare is a collaborative effort, where patient determination meets medical expertise to pave the way for recovery and restored well-being.
Patient Story #3: Confronting Frequent Cough in Bronchiectasis
The journey of a 30-plus-year-old woman sheds light on the persistent challenges posed by bronchiectasis, where the recurring symptom of frequent cough becomes a focal point of her medical narrative:
Frequent Cough: A Persistent Companion
For this patient, a recurrent and unrelenting cough became a regular occurrence in her life. Every month, she found herself seeking medical attention due to the frequency and intensity of her coughing episodes. The persistence of this symptom raised concerns and prompted her to seek answers for her health predicament.
Unraveling the Underlying Issue
A comprehensive evaluation of her condition unfolded a vital piece of the puzzle. Investigation of her phlegm indicated the presence of a bacterial infection. This revelation provided crucial insights into the underlying cause of her recurrent cough. The diagnosis of bronchiectasis explained the pattern of frequent infections and coughing episodes.
The Role of Antibiotics and Ongoing Management
Bronchiectasis often necessitates a multifaceted approach to management. Patients, like this young woman, may find themselves in need of regular antibiotics to address the recurring infections. The severity of her symptoms led to a collaborative decision involving her medical team, resulting in hospitalization for closer monitoring and intensified treatment.
A Comprehensive Assessment for Tailored Care
Careful assessment is a cornerstone of managing bronchiectasis. Medical professionals employ tools such as chest X-rays and blood tests to gauge the progression of the condition. Additionally, sending phlegm samples for culture testing offers insights into the specific bacterial and viral culprits behind each infection episode. This personalized approach ensures targeted treatment that aligns with the patient’s unique needs.
Navigating Recurrence: A Journey Together
For individuals battling bronchiectasis, recurring symptoms require ongoing attention and management. Frequent and prolonged coughing can take a toll on both physical and emotional well-being. The dedication of healthcare providers to tailor interventions, prescribe antibiotics as needed, and provide necessary hospitalization when warranted underscores the comprehensive care that patients require.
A Call for Vigilance and Empowerment
The journey of this patient emphasizes the significance of vigilance when faced with bronchiectasis. Frequent coughing episodes serve as a reminder of the condition’s complexities and the importance of collaborative efforts between patients and medical professionals. Empowered with knowledge and guided by expert care, individuals can navigate the challenges of bronchiectasis with determination and resilience.
Vaccination and Pulmonary Rehabilitation for Bronchiectasis Patients
Bronchiectasis patients stand to benefit immensely from proactive measures that safeguard their respiratory health. Two key pillars of such proactive care are vaccination and pulmonary rehabilitation:
Vaccination: A Shield Against Future Infections
The significance of vaccination cannot be overstated for individuals grappling with bronchiectasis. In fact, vaccination plays a pivotal role in reducing the risk of future infections by up to an impressive 70%. To provide comprehensive protection, I often recommend three specific types of vaccinations:
- Pneumococcal 13 Vaccination: This vaccination targets a bacterium called Streptococcus pneumoniae, which can cause severe infections, especially in those with compromised lung health.
- Influenza Vaccination: Given the vulnerability of bronchiectasis patients, safeguarding against the flu is crucial. Influenza vaccination helps mitigate the risk of this viral infection, which can exacerbate bronchiectasis symptoms.
- Pneumococcal 23 Vaccination: This additional pneumococcal vaccination complements the Pneumococcal 13 vaccination, reinforcing the protective shield against potential infections.
By ensuring completion of these three vaccinations, patients can bolster their lung defenses significantly. Vaccination serves as a proactive step in preventing infections that could further strain the respiratory system.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation and Chest Physiotherapy: Clearing the Pathways
The unique lung anatomy of bronchiectasis patients, often altered by scarring, can trap mucus and secretions in their airways. This provides a breeding ground for bacterial and viral invaders. To counteract this challenge, pulmonary rehabilitation and chest physiotherapy emerge as invaluable allies.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation: This structured program aims to enhance lung function and improve overall well-being. Tailored exercises and techniques help patients strengthen their respiratory muscles and optimize lung capacity. By doing so, bronchiectasis patients can experience improved lung clearance and a better ability to cope with daily activities.
Chest Physiotherapy: This specialized approach focuses on clearing the airways of accumulated mucus and secretions. By employing techniques like percussion, vibration, and breathing exercises, chest physiotherapy aids in expelling the trapped secretions. This not only eases breathing but also reduces the risk of infection by minimizing the welcoming environment for harmful microorganisms.
Empowerment Through Proactivity
As healthcare providers, our goal is to empower bronchiectasis patients to take charge of their respiratory health. By advocating for timely vaccinations and actively engaging in pulmonary rehabilitation or chest physiotherapy, individuals can significantly enhance their quality of life. These proactive steps, combined with expert guidance and care, equip patients with the tools to navigate the complexities of bronchiectasis with resilience and confidence.
Conclusion: Navigating Bronchiectasis for Better Breathing
Bronchiectasis can be complex, but understanding its signals and risks is key. Coughs, infections, and discomfort are markers that call for attention. Certain factors like low immunity or past infections increase the chances.
Diagnosing bronchiectasis involves history, exams, and scans. Once diagnosed, treatment is personalized. Antibiotics and interventions help manage symptoms and complications.
Preventing problems is vital. Vaccines shield against infections, and physiotherapy aids lung health. Together, these steps empower patients on their journey towards healthier breathing. Collaboration with doctors, sticking to treatments, and self-care lead the way to better days ahead.
If you require assistance for Bronchiectasis
you can schedule an appointment
with Dr Nurul HERE



































